Long vs Short Fiber
Long fiber reinforced thermoplastic and short fiber reinforced thermoplastic solutions are both utilized to achieve strong and stiff, high-performing injection-moldable solutions. Fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites offer many advantages over metals when it comes to part design. Choosing the right type of reinforcement (long vs. short) is critical to meet the physical demands and needs of your product.
At a high level, long fiber and short fiber reinforced solutions vary simply as that – fiber length within the pellets. Our long fiber products are produced using a pultrusion process in which continuous tows of fiber are pulled through an impregnation die (to introduce polymer and additive solutions) and then chopped to length (typically 12mm) in a pelletizer. In contrast, short fiber reinforced solutions are produced by introducing pre-chopped fibers (typically 1mm or less) into an extruder where the fibers are mixed with polymer and other additives.
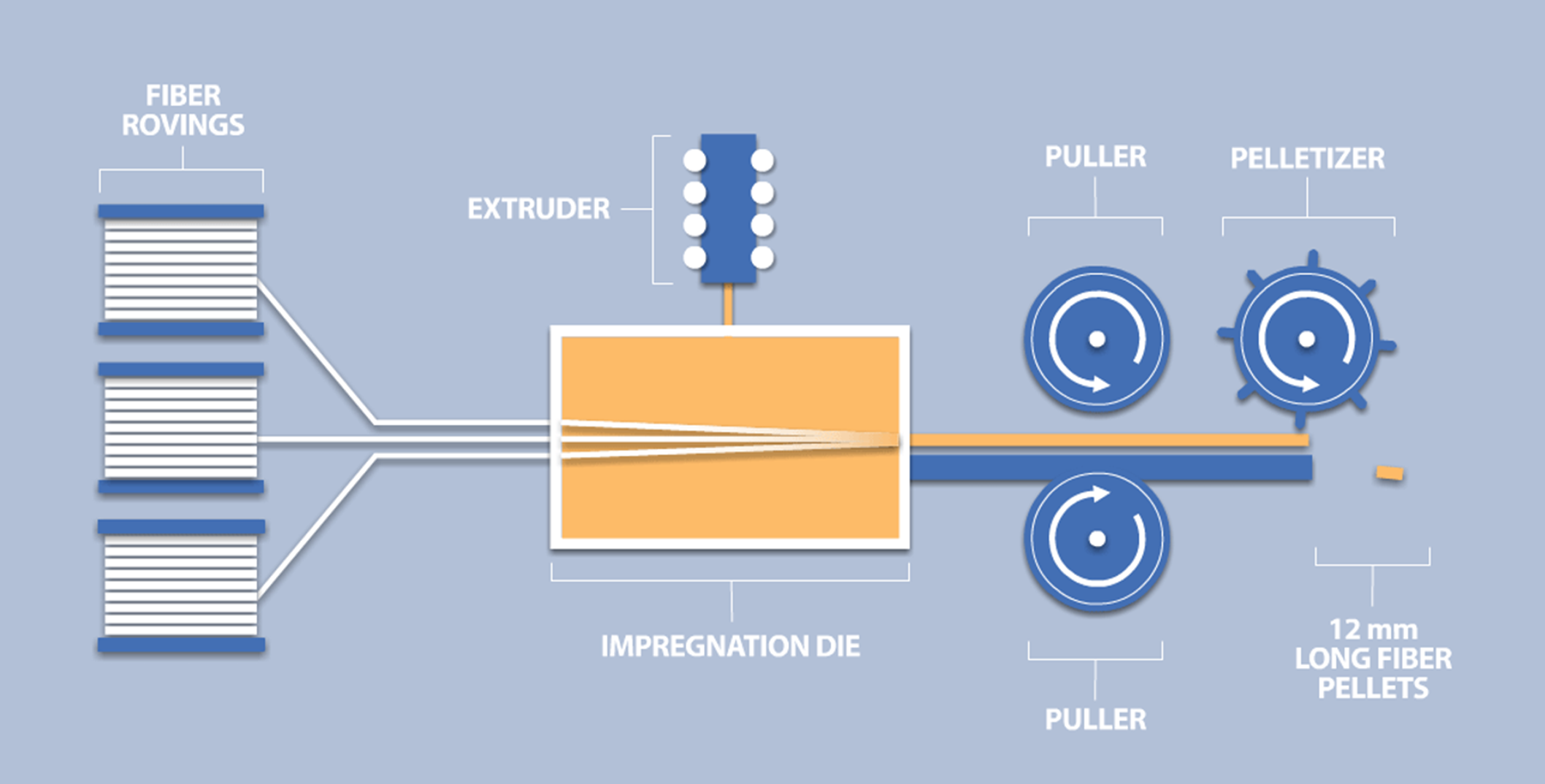
With long fiber reinforced solutions, the individual reinforcing fibers within each pellet are aligned parallel to each other and are exactly as long (usually 1/2 inch or 12 mm) as the pellet due to the unidirectional orientation of the fiber prior to pellet chopping. In contrast, short fiber reinforced thermoplastic materials contain reinforcing fibers of various short lengths (approximately 1mm in length on average) that are randomly orientated in the resin/pellet.
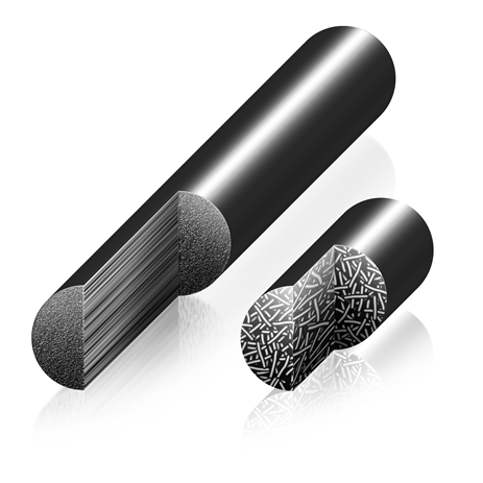

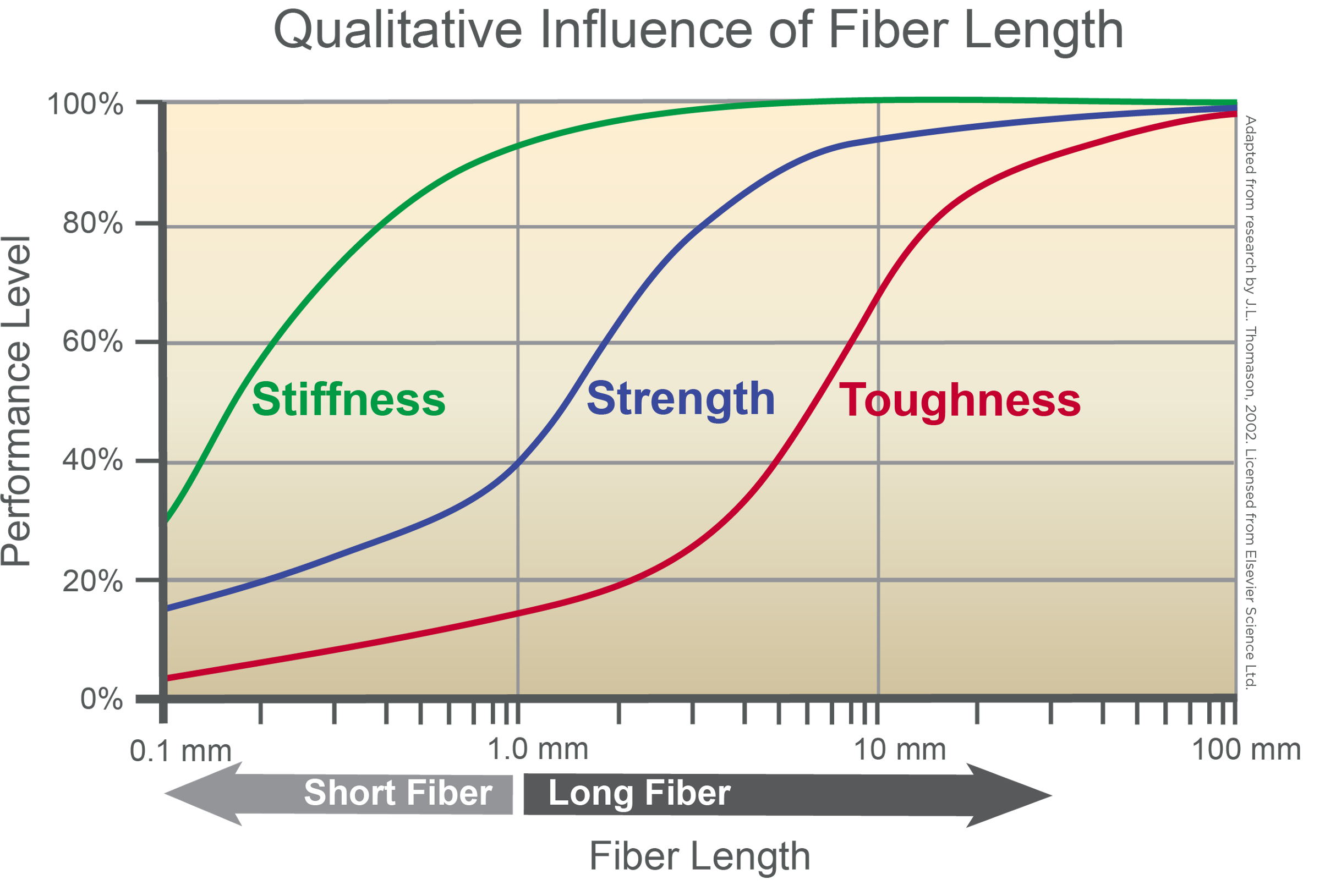
Since fiber in long fiber composites is continuous throughout the length of each cut pellet, long fiber materials have a higher fiber aspect ratio than short fiber filled plastics. Higher fiber aspect ratio provides the thermoplastic polymer with more ability to transfer energy to the stronger reinforcing fibers when the material comes under stress load and also to dissipate that energy over a wider area, therefore greatly improving impact performance. In addition to a gain in toughness performance LFTs also boost stiffness and strength as well.
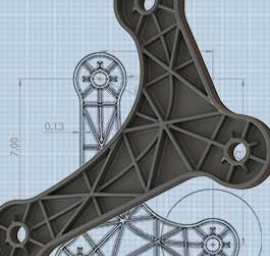
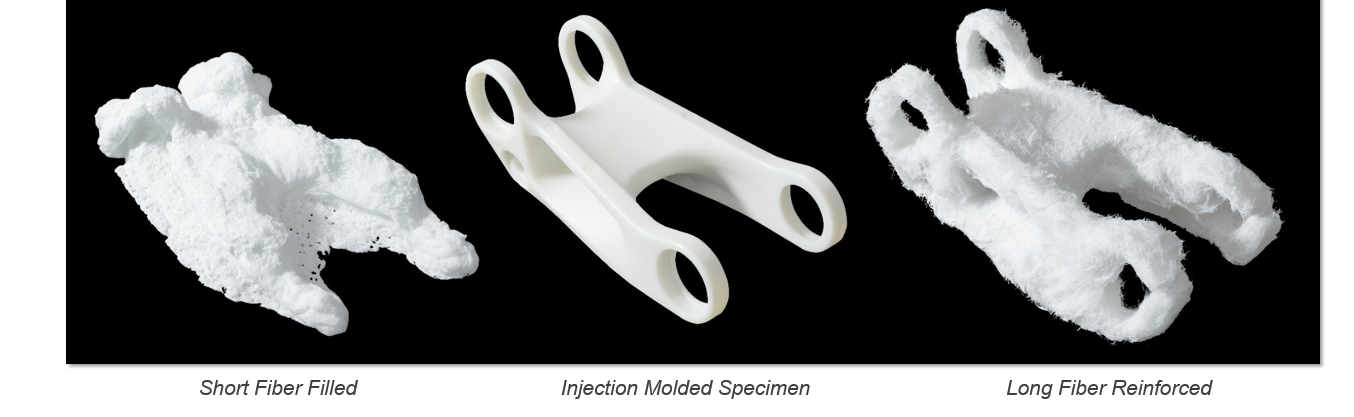
To highlight and show the longer fiber length entanglement and orientation in a geometry we have molded the same bicycle link (center) in both a long fiber reinforced solution and a short fiber reinforced solution. After a pyrolysis study, in which we burn away the polymer to study the remaining fiber, you can see how the structural skeleton of the long fiber part holds its shape and the short fiber part collapses on itself. This skeletal structure enables the efficient transfer of loads and gives long fiber thermoplastics a distinct advantage over short fiber alternatives.

Summary of Benefits
Long Fiber Reinforcement
- 0.5 in/12 mm long
- 0.12 in/3 mm diameter
- Parallel fibers run length of the pellet
- Fibers encapsulated with resin
- Significantly increased impact performance
- Boosted strength and stiffness properties
- Improved load carrying ability
- Better creep resistance
- Enhanced fatigue endurance
- Better dimensional stability
Short Fiber Reinforcement
- Pellets typically 0.12 in/3 mm long
- Fibers typically 0.04 in/1 mm long
- Random fibers varying in length and orientation
- More easily reprocessable